
Smart Beginnings 2022: A Review of Key OSEP Presentations
Purpose: The Office of Special Education Programs (OSEP) will showcase presentations from 2021 and 2022 on a range of topics designed to promote educational excellence for infants, toddlers, youth, and families of children with disabilities. These presentations are targeted to OSEP stakeholder audiences that include K-12 personnel, providers, teachers, administrators, families.
Event Goal: OSEP's Smart Beginnings event will cover topics that help families, providers, and leaders better support children with disabilities. OSEP leadership and subject matter experts will highlight resources ranging from early intervention at birth to secondary transition. During each presentation OSEP will disseminate information, resources, and strategies on IDEA topics to reach State personnel, LEA's, local service providers, schools, teachers, and families.
Should you have any questions on the resources provided each day, or the resources that will be highlighted after each presentation here on the website, please contact OSEP at smartbeginnings@ed.gov
Please note: The videos found in the resources range in length from 1 minute to 1.5 hours depending on the topic and the audience.
Day 1 - Videos
Tuesday, August 9, 2022
Parent Engagement Videos

Home Learning for Children with Significant Cognitive Disabilities (5:20)
Effective Stakeholder Engagement - Beyond a Data Reporting Requirement (1:28:30)
Parents and Systems Partnering to Address Difficult Times (1:29)
Transition Video
Part C / Family Engagement Videos

Empowering Parents of Young Children as Advocates and Leaders to Impact System Change (34:26)
Elevating Family Voice in Part C and Part B 619 Programs (30:00)
Back to Preschool and Kindergarten: Critical Considerations (30:00)
Using OSEP Fast Facts as a Stakeholder Engagement Tool(10:29)
Creating Equitable Access for Students with Disabilities Through the IEP Process (48:39)
Day 1 - Resources for Family Members and Advocates
Secondary Transition: Helping Students with Disabilities Plan for Post-High School Settings
- This self-paced module focuses on the transition process from high school to post-secondary settings. Among other topics, it discusses IEP planning, engaging students in the process so as to become better advocates for their own needs, and the importance of outside agencies such as vocational rehabilitation.
Secondary Transition: Student Centered Transition Planning
- This module will help users to better understand the benefits of student-centered transition planning, identify ways to involve students in collecting assessment information and developing goals, and be able to prepare students to actively participate in their own IEP meetings.
READY Tool: Readiness Evaluation of Transition to Adulthood for Deaf-Blind Youth
- The READY Tool helps a transition team, composed of an individual who is deaf-blind, parents, and professionals, determine essential activities that must be carried out during the transition process. The completed tool should be used to generate a plan of action and develop goals and objectives for the IEP and transition plans.
- This Brief describes how families and other members of Individualized Education Program (IEP) teams can help students get the supports they need to build their communicative competence in inclusive classrooms. Being able to communicate is an important skill for students with significant cognitive disabilities. Communication does not need to be oral. But it should be sufficient for conveying messages to others.
- Use this free online assessment to screen your child for risk of future reading difficulties.
Supporting Students with Reading Needs
- This toolkit, developed in collaboration with the Idaho State Department of Education, helps parents and families use everyday time together as an opportunity for learning and building reading skills.
The Role of the Family in IEP Development
- As a family member of a child with deaf-blindness, it is important for you to understand your role in this planning process. Here are some resources that clarify the role of the family in the development of Individualized Education Programs (IEPs).
NCDB Professional Development Webinar: Establishing Routines at Home
- This session provides a framework for working with families to support the development and implementation of home-based routines for children who are deaf-blind. It also addresses how to use individualized daily schedules to represent activities and routines in the home setting and capture those activities in experience stories and books.
- It is important for parents to know what paraprofessionals should be expected to do in inclusive classrooms. Parents should also know what qualities paraprofessionals should have, and what supports and training they need to be successful in their role. The purpose of this Brief is to address these points. It also pro-vides examples of appropriate use of paraprofessionals in inclusive classrooms and some red flags that might indicate a need to adjust paraprofessional support or training.
Day 1 - Resources for Part C & 619
Your Child's Move from Hospital to Home
- Before your infant leaves the hospital, you can take a number of steps to be sure needed supports are in place once your child is home. Referrals to community programs and early intervention services can begin while your infant is still in the hospital. You can play an important role in the discharge planning process by asking questions, sharing concerns, and obtaining key information about programs and supports you think will be useful for you and your infant.
Your Child's Move from Early Intervention to Preschool Special Education Services
- As your toddler approaches his or her third birthday, early intervention practitioners will work with you to plan your child’s transition from early intervention and, if potentially eligible, to preschool special education services. This transition involves key decisions about your child’s future. By communicating and collaborating with both the early intervention program staff and the preschool program staff, you can share information you need to actively participate in the transition planning process, share your concerns and preferences, and help your child adjust to the new setting and services.
Your Child's Move from Preschool Special Education to Kindergarten
- The transition to kindergarten is an important time in your and your child's life and you want to be as prepared as possible. Learn about kindergarten requirements, expectations, and routines before your child is enrolled. Work with the preschool program staff and ask for their support to access key information and participate in kindergarten transition strategies. Engaging in transition planning activities will help you to be more prepared to support your child’s and your family’s adjustment to the new kindergarten setting in your local school.
Ares' Family Story: How Virtual Visits Work
- One of several videos of family stories about virtual visits. If you're new to EI/ECSE and want to understand how virtual visits work, listen to nine-month-old Ares' family story.
- Children learn best by being active participants in everyday activities like meal times, bath times, and playing with toys. Sometimes children with disabilities need help participating in a learning activity. We call this support an adaptation or modification. Adaptations and modifications involve changes to the space, materials, activity, or instruction to increase a child’s ability to participate in an activity.
Supporting Family Leaders: What May Keep Families From Getting Involved in Leadership?
- This is one of several videos in a series on Conversations with Family Leaders. Sherri Britt Williams shares her experience with early intervention when her twin girls were infants and her opportunity to serve as a family leader in EI and Preschool Special Education.
Noah and Pop-Pop Go To Preschool
- One of several videos of family stories about virtual visits. In this video, mother and grandfather to Noah, Sarah and Randy, describe their family's approach to supporting Noah in attending virtual preschool.
Adult-and-Child Shared Reading
- Adult-child shared reading experiences provide rich opportunities for mutually beneficial teacher and child interactions. When teachers spend time reading with young children in ways that encourage their active participation, they help children strengthen their listening skills, develop their language abilities, and increase their knowledge about the world.
Screening for Emergent Literacy During Well Visits
- This infographic explores The Reading House (TRH), a children’s book designed to assess emergent skills in 3- to 4-year-old children during pediatric wellness visits.
Day 2 - Videos
Wednesday, August 10, 2022
Teacher Preparation, Recruitment, and Retention Video

Sparking a Revolution in Special Education - Reimagining Preparation and Practice -- Large Group Panel presentation from the OSEP 2022 Leadership and Project Directors Conference (1:29:01)
Strategies of Remedy and Recovery (Including MTSS) Videos

Using Positive Behavioral Interventions and Support to Ensure Racial Equity in School Discipline (33:14)
Back to Preschool and Kindergarten: Critical Considerations (28:46)
Screening Videos

Early Screening for Dyslexia/Reading Disability: Preliminary Findings (5:16)
A Discussion on on Screening from the National Center on Improving Literacy (24:36)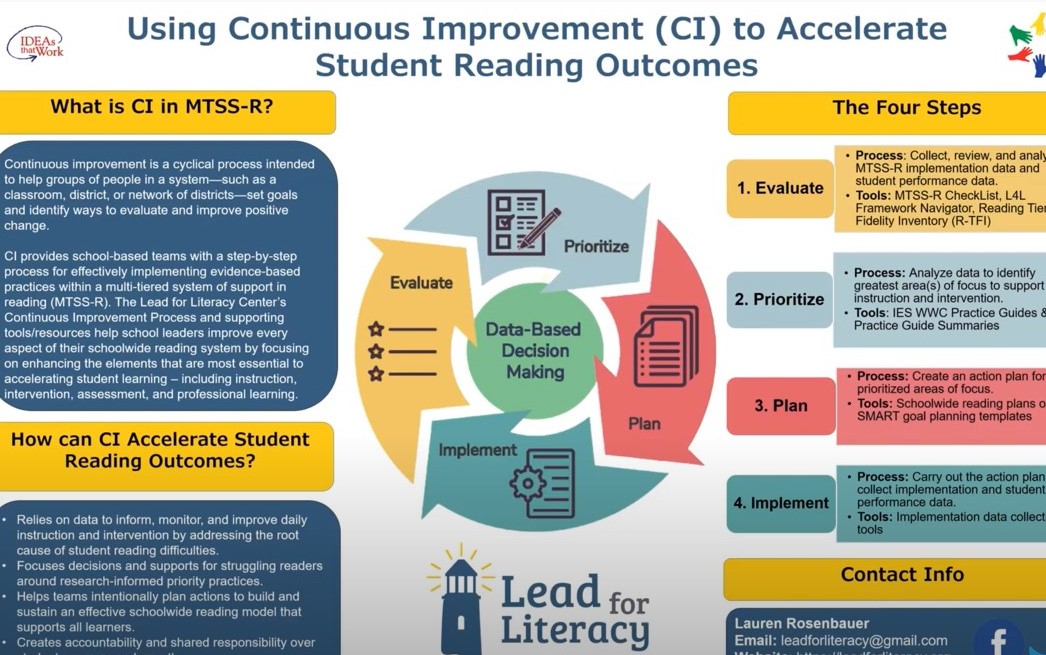
Using Continuous Improvement to Accelerate Student Reading Outcomes (5:50)
Systematic Screening: The Practicalities of Using Screening Data to Inform Instruction (1:17:58)
Day 2 - Resources for Part B Administrators & Leaders
Teacher Induction: Providing Comprehensive Training for New Special Educators
- This module emphasizes the importance of administrative support for beginning special education teachers. It also demonstrates how teacher support can increase the teacher's effectiveness in the classroom
Teacher Retention: Reducing the Attrition of Special Educators
- This module highlights the key elements for school administrators who seek to support special educators and increase teacher retention
Educator Shortages in Special Education: A Toolkit for Developing Local Strategies
- This resource is organized around the guiding principle that short-term strategies to meet immediate demand must be intentionally paired with long-term, systematic strategies to attract, prepare, and retain effective special education teachers to create comprehensive shortage solutions
An Opportunity to Invest in the Educator Workforce
- This brief is intended to help state education agencies and local education agencies strategically leverage federal recovery funds to attract, prepare, and retain educators
- This brief offers concrete ways teacher candidates can be leveraged to better support veteran teachers during the shift to distance learning or new education models.
Highlighting Key Considerations for Literacy Screening and Assessment
- In this webinar David Fainstein and Lauren Artzi from the Lead for Literacy Center discuss types of data that inform reading instruction and review the quality indicators of useful data and assessments. They focus discussion on the purpose and process of screening for reading difficulties in both traditional and virtual settings and highlight implementation considerations related to the screening process.
Best Practices in Universal Screening
- There is broad agreement that schools should implement early screening and intervention programs. State legislation generally favors the use of universal screening within schools across grades K-2.
Core Considerations for Selecting a Screener
- There are many available screeners for reading and other education or social-emotional outcomes. This brief outlines important things to consider when choosing and using a screener.
Ten Ways Schools Can Foster Belonging Among Students with and Without Disabilities
- To ensure students with disabilities benefit from their school experiences, schools need to going beyond just inclusion in the classroom experience and instruction and promote a deep sense of belonging. This suite of resources includes a 60-minute video discussing the dimensions of belonging and a planning resource to support schools as they develop ecosystems that promote belonging among students with and without disabilities.
- There are many myths about including students with the most significant cognitive disabilities in general education classrooms. This Brief debunks six of them, including students with the most significant cognitive disabilities have too many challenges to benefit from inclusion in the general education classroom.
- The purpose of this brief is to answer the question of what access to and progress in the general education curriculum means for students with the most significant cognitive disabilities. This brief also confirms that federal education laws require that students who participate in the AA-AAAS receive instruction in the same grade-level content as all other students. It is the achievement expected on the same grade-level content that can be reduced in breadth, depth, and complexity. This information is very important in the discussion of a student’s educational setting. Often the myth that these students need an alternate curriculum is used incorrectly as an argument against educating the student in the general education classroom.
Creating Communities of Belonging for Students With Significant Cognitive Disabilities
- Developed to directly address the creation of school communities in which each and every student is included in all aspects of everyday school life, Creating Communities of Belonging for Students with Significant Cognitive Disabilities describes ten dimensions of belonging. This is a "ready to use" resource that includes a mini guide for each dimension of belonging that defines the dimension, provides snapshots of what it would look like, presents steps schools could take to promote change, and suggests areas of reflection for members of the school community. Belonging matters for everyone - check out this resource to support that outcome for each student in your school community!
PROGRESS Center Special Education Online Training Courses
- These online courses are intended to build in-service and pre-service educator and administrator knowledge on how to develop and implement high-quality educational programming for students with disabilities. These courses include self-paced learning content, related resources, and a certificate of completion.
- This video highlights six high-leverage, evidence-based practices shown to support implementation of high-quality instructional programming for students with and at risk for disabilities regardless of their identified disability category or grade span. An instructional practice brief is available for each identified instructional practice.
Day 2 - Resources for Part C & 619 Administrators and Other Leaders
Remote Screening, Evaluation, and Assessment
- Many assessment practices can be successfully implemented even when the practitioner cannot be in the same room with the child and family such as during the COVID-19 pandemic. The resources included here are designed to help states, programs, and local practitioners examine and answer difficult questions about remote screening, evaluation, and assessment.
Screening Tools for Children Birth to Age Five Years with Potential for Remote Administration
- This resource is a list of screening tools that can be completed remotely when the practitioner cannot be in the room with the child. Screening tools assess the possibility of a disability or delay and whether more extensive assessment may be necessary. These tools can be administered through parent/caregiver questionnaires, through interview, and/or by observation of the child without the administration of direct, structured tasks. These tools include screeners that provide information in multiple domains as well as screeners that focus on one specific area such as speech or motor development.
Indicators of High-Quality Inclusion
- Four sets of indicators of high-quality inclusion, designed by a group of national partners, are available to support state leaders, local administrators and front-line personnel in the early care and education system providing programs and services to children, ages birth through five and their families. The State Indicators, Community Indicators, Local Program Indicators, and Early Care and Education Environment Indicators detail the key elements needed to be in place for high-quality infrastructure and practices.
Family Engagement: Collaborating with Families of Students with Disabilities
- This self-paced module addresses the importance of engaging the families of students with disabilities in their child’s education. It highlights some of the key factors that affect these families and outlines some practical ways to build relationships and create opportunities for involvement.
Creating an Inclusive School Environment: A Model for School Leaders
- This self-paced module offers a general overview of the concepts that principals should consider when creating inclusive schools.
Secondary Transition: Interagency Collaboration
- This self-paced module defines and discusses the purpose of interagency collaboration and addresses the importance of partnering with agencies to improve outcomes for students with disabilities who are transitioning from high school.
Day 2 - Resources for Part B Educators
Comprehensive Inclusive Education: General Education and the Inclusive IEP
- The comprehensive inclusive education planning process described in this article is intended to support the creation and provision of a curricular and instructional program based on the acknowledgment that each child is a general education student. That the general education curriculum and routines and the Individual Education Program (IEP) comprise a student’s full educational program. That the IEP for a student qualifying for special education services is not the student’s curriculum.
TIP # 12: Standards-based Grading and Report Cards in Inclusive Elementary and Middle Schools
- This TIPS sheet provides guidance on how to provide fair and accurate grades for students with significant cognitive disabilities in inclusive settings. It also addresses ways to report standards-based grades for students with significant cognitive disabilities.
- This toolkit helps educators and parents learn about how screening can help determine which students may be at risk for reading difficulties.
Understanding Screening: Overall Screening and Assessment
- Assessment is a process of collecting information. Screening is an assessment process that helps teachers identify students who are at risk for not meeting grade-level learning goals.
How We Learn to Read: The Critical Role of Phonological Awareness
- Phonological awareness involves being able to recognize and manipulate the sounds within words. This skill is a foundation for understanding the alphabetic principle and reading success. There are several ways to effectively teach phonological awareness to prepare early readers, including: 1) teaching students to recognize and manipulate the sounds of speech, 2) teaching students letter-sound relations, and 3) teaching students to manipulate letter-sounds in print using word-building activities.
Day 3 - Videos
Thursday, August 11, 2022
Science of Reading

Can the Science of Reading Fix Everything? -- Large Group Panel presentation from the OSEP 2022 Leadership and Project Directors Conference (1:30:54)
Instruction for Students with Significant Cognitive Disabilities

Lessons Learned During the Pandemic That Affect In-Person Learning (27:10)
Home Learning for Children with Significant Cognitive Disabilities (5:20)
Day 3 - Resources for Part C & 619 Providers
Early Care and Education Environment Indicators and Elements of High-Quality Inclusion
- The Early Childhood Education Environment (ECEE) Indicators detail the key elements that are necessary for implementing high-quality inclusive practices in early childhood settings. They are designed to assist personnel in providing effective supports and services to young children with disabilities. It is assumed that all federal and state legal requirements are in place. These indicators are not meant to examine federal and state requirements. They are intended to enhance high-quality inclusive practices implemented by early care and education personnel.
Naturalistic Instruction Practices
- Naturalistic instruction practices are used during everyday classroom activities to support and encourage child engagement in child-initiated activities and child behavioral elaborations in the activities. Teachers can promote child participation and learning in everyday classroom activities by providing interest-based activities, responding positively to children's initiations, and interacting in ways that encourage children to build on and expand their current capabilities.
- Teachers can support children’s participation, independence, and learning in everyday classroom activities by using a practice called “following the child’s lead.” Child-initiated interactions are a key characteristic of this practice. Following a child’s lead involves planning and adjusting classroom activities based on children’s interests, facilitating children’s interactions with the social and nonsocial environment, and supporting children’s choices to transition from one activity to another.
Embedded Instruction Practices
- Embedded instruction involves multiple, brief teaching interactions between a teacher and child during everyday classroom activities. By identifying functional behavior targets, selecting classroom activities best suited for embedded learning opportunities, and using planned and intentional instructional strategies, teachers can help children learn new behavior for participating in classroom activities throughout the day.
Nursery Rhymes and Child Interactions
- Using rhymes during interactions with toddlers helps them explore the sounds and purposes of language. Songs, finger plays, and rhyming games provide opportunities for toddlers to have fun during interactions with adults while building skills for understanding and using language.
- Throughout the preschool years, young children continue to acquire and use new and more complex language abilities as part of interactions with other children and adults. You can boost children's language learning by increasing their opportunities to engage in conversations and by both encouraging and supporting their language use during everyday classroom activities



